
300K;
Eg=6.2 eV;
EM-L= 6.9 eV;
Eso = 0.019 eV;
Ek= 7.2 eV
For details see Christensen & Gorczyca (1994)

Kobayashi et al. (1983)

| Wurtzite(hexagonal) crystal structure | Remarks | Referens | |
| Energy gaps, Eg | 6.026 eV | 300 K | Guo & Yoshida (1994) Teisseyre al. (1994) |
| 6.2 eV | 300 K, absorption (excitonic contribution near direct edge) |
Yamashita et al. (1979) | |
| 6.23 eV | 77 K, absorption (excitonic contribution near direct edge) |
Yamashita et al. (1979) | |
| 6.28 eV | 300 K, from excitonic edge assuming exciton binding energy of 75meV |
Roskovcova & Pastrnak (1980) |
 c (Γ6v - Γlc),
both states being split by crystal field interaction . Yamashita
et al. (1979)
c (Γ6v - Γlc),
both states being split by crystal field interaction . Yamashita
et al. (1979) | Conduction band | Remarks | Referens | |
| Energy separation between Γ valley and M-L valleys | ~0.7 eV | 300 K | Goldberg (2001) |
| Energy separation between M-L valleys degeneracy | 6 eV | 300 K | |
| Energy separation between Γ valley and K valleys | ~1.0 eV | 300 K | |
| Energy separation between K valley degeneracy |
2 eV |
300 K | |
| Valence band | |||
| Energy of spin-orbital splitting Eso | 0.019 eV | 300 K | Goldberg (2001) |
|
Effective conduction band density of states |
6.3 x 1018 cm-3 | 300 K | |
|
Effective valence band density of states |
4.8 x 1020 cm-3 | 300 K |
 |
AlN, Wurtzite. Band structure. Important minima of
the conduction band and maxima of the valence band. 300K; Eg=6.2 eV; EM-L= 6.9 eV; Eso = 0.019 eV; Ek= 7.2 eV For details see Christensen & Gorczyca (1994) |
 |
AlN, Wurtzite. Band structure calculated with an a semi-empirical
tight binding method. Kobayashi et al. (1983) |
| Energies of symmetry points |
Remarks | Referens | |
| E (Γ1v) | -18.40 (-14.43) eV | calculated , see Band structure. Data in brackets Huang & Ching (1985) |
zKobayashi et al. (1983) |
| E (Γ3v) | -7.10 (-4.68) eV | ||
| E (Γ5v) | -1.22(-0.60) eV | ||
| E (Γ6v , Γ1'v) | 0.00 eV | ||
| E (Γ1c) | 6.2 (6.25) eV | ||
| E (Γ3c) | 8.92 (9.38) eV | ||
| E (Γ6c , Γ1'c) | 13.0 eV | ||
| E (Γ1'3'v) | -7.52 (-4.26) eV | ||
| E (Γ24v) | -1.97 (-1.06) eV | ||
| E (Γ13v) | -1.87 (-1.03) eV | ||
| E (Γ13c) | 9.99 (9.40) eV | ||
| E (Γ1'3'c) | 13.53 eV |
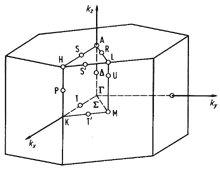 |
Brillouin zone of the hexagonal lattice. |
| Eg = Eg(0) - 1.799 x 10-3
x T2/(T + 1462) |
(eV) | Guo & Yoshida (1994) Teisseyre al. (1994) |
| Eg (300 K) = 6.026 eV |
 |
AlN, Wurtzite. Optical band gap versus temperature. Guo & Yoshida (1994) |
| dEg/dP = 3.6 x 10-3 (eV kbar-1) | Gorczyca & Christensen (1993) |
| Eg = Eg(0) + 3.6 x 10-3 P - 1.7 x 10-6 P2 (eV) | Van Camp et al. (1993) |
| EM = EM(0) + 7.5 x 10-4 P + 1.0 x 10-6 P2 (eV) | |
| EL = EL(0) + 8.0 x 10-4 P + 6.9 x 10-7 P2 (eV) | |
| Ek = Ek(0) + 6.3 x 10-4 P + 1.7 x 10-6 P2 (eV) |
| InN/AlN(0001) | Referens | |
| Conduction band discontinuity | ΔEc = 2.7 eV | Martin et al. (1996) |
| Valence band discontinuity | ΔEv = 1.8 eV | |
| GaN/AlN (0001) | ||
| Conduction band discontinuity | ΔEc = 2.0 eV | Martin et al. (1996) |
| Valence band discontinuity | ΔEv = 0.7 eV | |
| SiC/AlN (0001) | ||
| Valence band discontinuity | ΔEv = 1.4 eV | King et al. (1996) |
| Wurtzite AlN | Remarks | Referens | |
| Effective electron mass of density of states for Γ valley me | 0.40 mo | 300 K, Teoretical estimations of the electron effective mass anisotropy | Xu and Ching (1993) |
| Wurtzite AlN | Remarks | Referens | |
| Effective hole masses (heavy) for kz direction mhz for kx direction mhx |
3.53 mo 10.42 mo |
300 K | Suzuki & Uenoyama (1996) |
| Effective hole masses (light) for kz direction mlz for kx direction mlx |
3.53 mo 0.24 mo |
300 K | |
| Effective hole masses (split-off band) for kz direction msoz for kx direction msox |
0.25 mo 3.81 mo |
300 K | |
| Effective mass of density of state mv: | 7.26mo | 300 K |
| Native donors: |
Si, Mg (ionization energy ΔE ~= 1 eV) |
| Donors: |
C, Ge, Se |
| Acceptors: |
C, Hg |
| Ionization energies (Et-Ec) |
||
| d1 is the donor level of N vacancies (VN) | 0.17 eV | Tansley & Egan (1992); Chu et al. (1967); Francis and Worell (1976); Jenkins and Dow (1989); Mohammad et al. (1995); Boguslawski et al. (1996); Gorczyca et al. (1997) |
| d2 is the donor level of N vacancies (VN) | 0.5 eV | |
| d3 is the donor level of N vacancies (VN) |
0.8-1.0 eV |
|
| d4 is the donor levels of C in Al sites (CAl) | 0.2 eV | |
| d5 is the donor levels of N in Al sites (NAl) | 1.4-1.85 eV | |
| d6 is the donor levels of Al in N sites (AlN) | 3.4-4.5 eV |
| Ionization energies (Ev-Et) |
||
| a1 is the acceptor levels of Al vacancies (VAl) | 0.5 eV |
Tansley & Egan (1992); Chu et al. (1967); Francis and Worell (1976); Jenkins and Dow (1989); Mohammad et al. (1995); Boguslawski et al. (1996); Gorczyca et al. (1997) |
| a2 is the acceptor levels of C in N sites (CN) | 0.4 eV |
|
| a3 is the acceptor levels of Zn in Al sites (ZnAl) | 0.2 eV |
|
| a4 is the acceptor levels of Mg in Al sites (MgAl) | 0.1 eV |
 |
AlN, Wurtzite. Level positions in the forbidden gap of AlN.
Tansley & Egan (1992) |