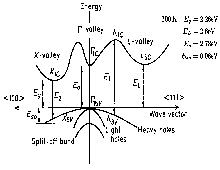
Important minima of the conduction band and maxima of the valence band. 300 K Eg = 2.26 eV
EL = 2.6 eV
Eo = 2.78 eV
Eso = 0.08 eV
| Energy gap | 2.26 eV |
| Energy separation Eo (Γ1c - Γ15ν) | 2.78 eV |
| Energy spin-orbital splitting | 0.08 eV |
| Intrinsic carrier concentration | 2 cm-3 |
| Effective conduction band density of states | 1.8·1019 cm-3 |
| Effective valence band density of states | 1.9·1019 cm-3 |
 |
Band structure and carrier concentration of GaP. Important minima of the conduction band and maxima of the valence band. 300 K Eg = 2.26 eV EL = 2.6 eV Eo = 2.78 eV Eso = 0.08 eV |
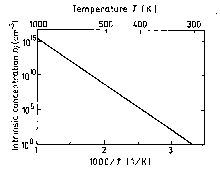 |
The temperature dependence of the intrinsic carrier concentration. |
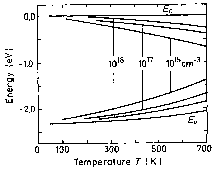 |
Fermi level versus temperature for different concentrations of shallow donors and acceptors. |
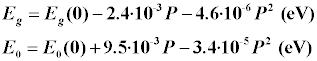 ,
,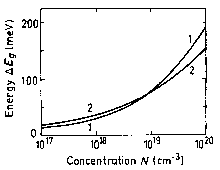 |
Energy gap narrowing versus donor (curve 1) and acceptor (curve 2) doping density, T= 300 K, (calculated according Jain et al. [1990]). |
| Electrons: | |
| The surfaces of equal energy are ellipsoids (X-valley) | |
| ml = 1.12mo | |
| mt = 0.22mo | |
| Effective mass of density of states | |
| mc=(9mlmt2)1/3 | mc=0.79mo |
| Effective mass of conductivity | mcc=0.35mo |
| For Γ-valley | mΓ = 0.09mo |
| For L-valley | ml = 1.2mo |
| mt = 0.15mo | |
| Holes: | |
| Heavy | mh = 0.79mo |
| Light | mlp = 0.14mo |
| Effective mass of density of states | mv = 0.83mo |
| Sp | Sep | Tep | Lip | GeGa | SiGa | SnGa | LiGa |
| 0.107 | 0.105 | 0.093 | 0.091 | 0.204 | 0.085 | 0.072 | 0.061 |
| Gep | Cp | Sip | BeGa | CdGa | MgGa | ZnGa |
| 0.265 | 0.0543 | 0.210 | 0.0566 | 0.1022 | 0.0599 | 0.0697 |
| Impurity | Position in the forbidden gap |
| Op(donor) | Ec - 0.89 (eV) |
| Cr (acceptor) | Ec - 1.2 (eV) |
| Ec - 0.5 (eV) | |
| Radiative centers(Baegh and Dean[1976]) | |
| N | Ev + 0.008 (eV) |
| ZnGa - Op | Ec - 0.3 (eV) |
| Capture cross section for electrons to neutral Zn-O complex (at 300 K) | σn~(1.5÷4.5)·10-16 (cm2) |
| Capture cross section for holes to negative Zn-O complex (at 77 K): | σp ~ 5·10-17 (cm2 |
| CdGa - Op | Ec - 0.40 (eV) |
| Mg - O | Ec - 0.14 (eV) |